The circulatory system is the route by which the cells in your body get the oxygen and nutrients they need, but blood is the actual carrier of the oxygen and nutrients. Blood is made mostly of plasma, which is a yellowish liquid that is 90% water. In addition to the water, plasma contains salts, sugar (glucose), and other substances. And, most important, plasma contains proteins that carry important nutrients to the body’s cells and strengthen the body’s immune system so it can fight off infection.
The average man has between 10 and 12 pints of blood in his body. The average woman has between 8 and 9 pints. To give you an idea of how much blood that is, 8 pints is equal to 1 gallon (think of a gallon of milk).
What is blood?
Blood is actually a tissue. It is thick because it is made up of a variety of cells, each having a different job. In fact, blood is about 80% water and 20% solid.
Blood is made mostly of plasma, but 3 main types of blood cells circulate with the plasma:
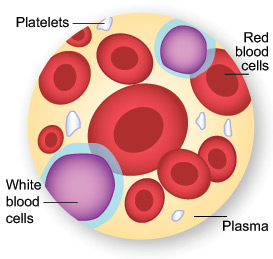 Platelets help the blood to clot. Clotting stops the blood from flowing out of the body when a vein or artery is broken. Platelets are also called thrombocytes.
Platelets help the blood to clot. Clotting stops the blood from flowing out of the body when a vein or artery is broken. Platelets are also called thrombocytes.- Red blood cells carry oxygen. Of the 3 types of blood cells, red blood cells are the most plentiful. In fact, a healthy adult has about 35 trillion of them. The body creates these cells at a rate of about 2.4 million a second, and they each have a life span of about 120 days. Red blood cells are also called erythrocytes.
- White blood cells ward off infection. These cells, which come in many shapes and sizes, are vital to the immune system. When the body is fighting off infection, it makes them in ever-increasing numbers. Still, compared to the number of red blood cells in the body, the number of white blood cells is low. Most healthy adults have about 700 times as many red blood cells as white ones. White blood cells are also called leukocytes.
Blood also contains hormones, fats, carbohydrates, proteins, and gases.
What does blood do?
Blood carries oxygen from the lungs and nutrients from the digestive tract to the body’s cells. It also carries away carbon dioxide and all of the waste products that the body does not need. (The kidneys filter and clean the blood.) Blood also
- Helps keep your body at the right temperature
- Carries hormones to the body’s cells
- Sends antibodies to fight infection
- Contains clotting factors to help the blood to clot and the body’s tissues to heal
Blood types
There are 4 different blood types: A, B, AB, and O. Genes that you inherit from your parents (1 from your mother and 1 from your father) determine your blood type.
Blood is always being made by the cells inside your bones, so your body can usually replace any blood lost through small cuts or wounds. But when a lot of blood is lost through large wounds, it has to be replaced through a blood transfusion (blood donated by other people). In blood transfusions, the donor and recipient blood types must be compatible. People with type O blood are called universal donors, because they can donate blood to anyone, but they can only receive a transfusion from other people with type O blood.
See also on this site:
See also on other sites:
MedlinePlus
https://medlineplus.gov/blooddisorders.html
Blood Disorders (Hematologic diseases)
https://medlineplus.gov/bloodclots.html
Blood Clots (Hypercoagulability)
Updated August 2016